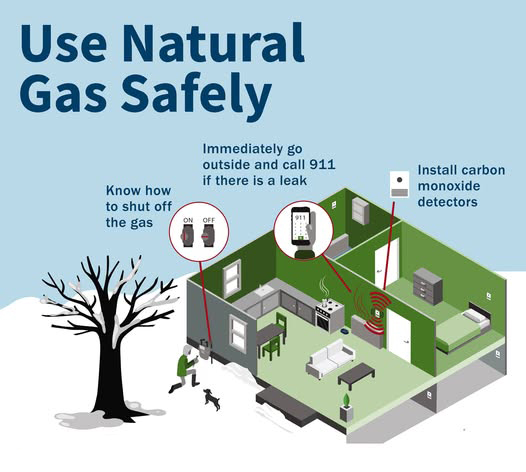
Natural gas safety is a critical component of protecting both people and structures. Gas-powered appliances, heating systems, and fuel lines are common in residential and commercial occupancies and are often located in close proximity to fire alarm, security, and other life safety systems. As a result, life safety and property protection professionals must be able to recognize conditions that indicate a potential gas leak, understand emergency shutoff procedures, and know when immediate evacuation and notification of emergency services is required. Prompt, informed action can prevent fires, explosions, and serious injuries, making gas awareness an essential professional responsibility.
Recognizing hazardous conditions is a key part of this responsibility. Indicators such as unusual odors, damaged or corroded piping, improperly vented appliances, or unexplained system troubles should never be ignored during an installation, inspection, or service call. Technicians are often among the most technically trained individuals to enter a premises, and their ability to identify potential gas-related risks and respond appropriately can protect occupants, property, and first responders.
Prevention and system integration are equally important. Carbon monoxide detection plays a vital role in identifying dangerous conditions that may not be immediately apparent, particularly in occupied spaces where gas appliances are in regular use. Proper installation, placement, testing, and ongoing maintenance of carbon monoxide detectors should be treated as a core life safety function—not an optional add-on. Integrating these devices correctly into broader life safety systems strengthens early warning capabilities and improves overall protection.
By reinforcing safe practices during system design, installations, inspections, and service visits, life safety and property protection professionals help reduce risk, safeguard property, and uphold the industry’s commitment to protecting lives. In Louisiana, where reliability and professionalism are central to public trust, natural gas safety awareness remains a vital part of comprehensive life safety planning.